Understanding Electrolytes and Their Importance
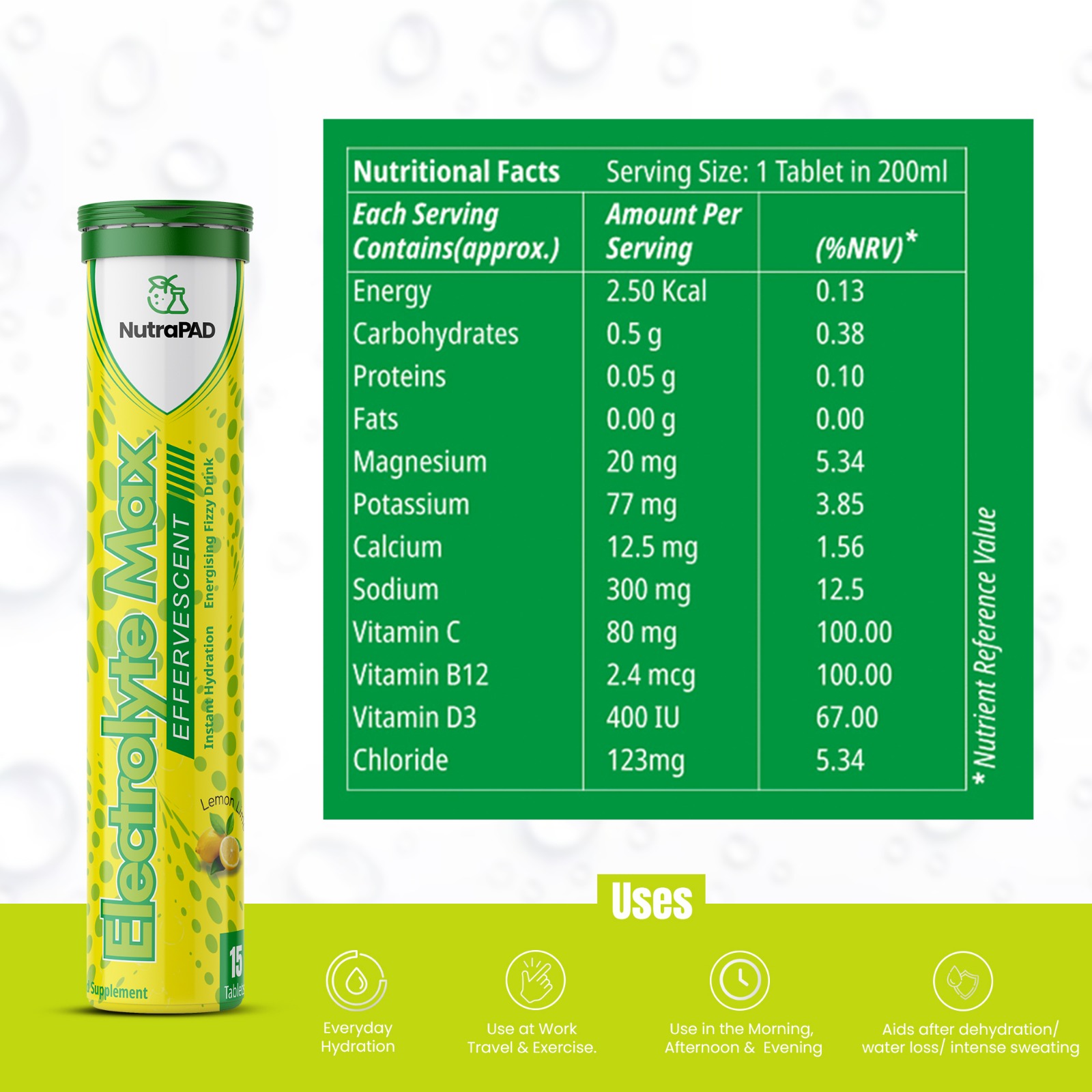
Electrolytes are essential minerals—such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium—that carry an electric charge and play critical roles in maintaining numerous physiological functions. They are vital for:
- Fluid Balance: Regulating the distribution of water within the body.
- Nerve Function: Transmitting nerve impulses essential for communication between the brain and body.
- Muscle Contraction: Facilitating the contraction and relaxation of muscles, including the heart.
- pH Level Maintenance: Keeping the body’s acid-base balance within a narrow, healthy range.
Roles of Specific Electrolytes
- Sodium (Na⁺): Maintains fluid balance, supports nerve signaling, and is crucial for muscle contractions.
- Potassium (K⁺): Regulates heart rhythm, aids in nerve transmission, and is essential for muscle function.
- Calcium (Ca²⁺): Strengthens bones and teeth, enables blood clotting, and supports muscle contractions.
- Magnesium (Mg²⁺): Involved in over 300 biochemical reactions, including energy production, muscle and nerve function, and blood glucose control.
Recommended Daily Allowances (RDAs)
The daily intake recommendations for these electrolytes vary based on age, gender, and life stage. General guidelines for adults are:
- Sodium: Less than 2,300 mg per day.
- Potassium: 2,300 mg to 3,400 mg per day, depending on age and gender.
- Calcium: 1,000 mg to 1,300 mg per day, depending on age and gender.
- Magnesium: 360 mg to 420 mg per day, depending on age and gender.
These values are general recommendations; individual needs may vary.
Conditions Requiring Electrolyte Supplementation
Electrolyte supplementation becomes crucial in situations where the body’s balance is disrupted, such as:
- Dehydration: Caused by inadequate fluid intake, excessive sweating, or high temperatures.
- Diarrhea and Vomiting: Lead to significant loss of fluids and electrolytes, increasing the risk of dehydration.
- Intense Physical Activity: Results in substantial electrolyte loss through sweat.
In such scenarios, replenishing electrolytes is vital to prevent complications like muscle cramps, fatigue, and, in severe cases, heart rhythm disturbances.
Scientific Research on Electrolyte Supplementation
Research underscores the importance of electrolyte replenishment in managing dehydration and related conditions. For instance, oral rehydration therapy (ORT) utilizes solutions containing electrolytes to effectively treat dehydration resulting from diarrhea. ORT has been shown to decrease the risk of death from diarrhea by up to 93%.
Furthermore, studies indicate that while most individuals obtain sufficient electrolytes through a balanced diet, supplementation is beneficial during intense physical activity or illness involving significant fluid loss.
Our Electrolyte and Vitamin Supplement
Our tablets are formulated to provide essential electrolytes—sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium chloride—along with vitamins C and D3, supporting overall health and aiding in the maintenance of vital bodily functions.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking other medications.
| Choose Your Flavour | Lemon & Lime, Mango Orange, Pink Lemonade, Cola |
|---|
Shipping & Return
● Free Royal Mail Tracked 48 shipping is available for domestic orders (within the U.K.) over £15.
● Under £15 and within the U.K., standard shipping is £1.99.
● You will receive your tracking number when your order ships in an email.
Expedited Shipping
We also offer expedited and tracked domestic delivery for £4.50 per order via DHL 24 Hour Tracked service.
Returns
Unfortunately, due to the nature of our product we are unable to accept returns of any opened tubes. Returns for other reasons, for example damaged products, will be considered on a case-by-case basis.
















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.